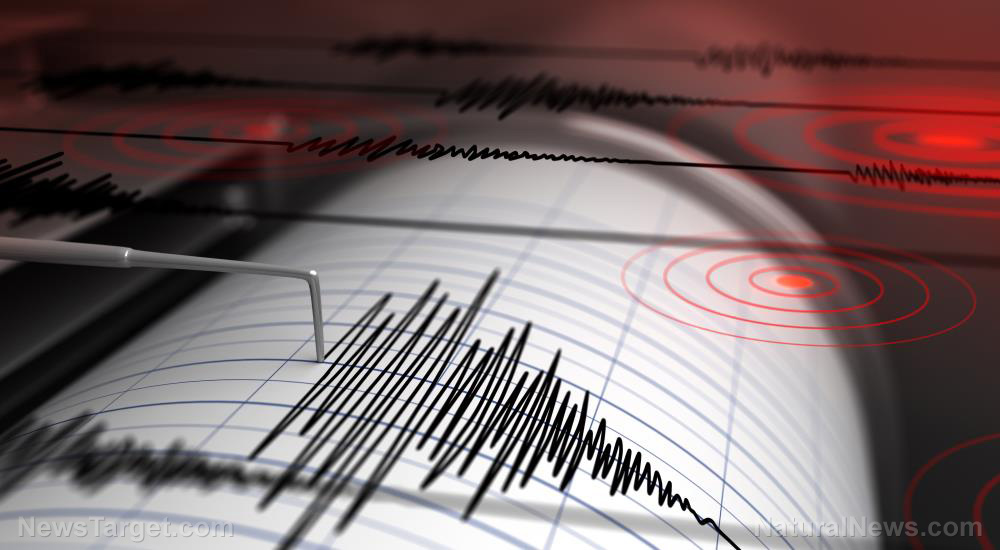
On the night of August 17, 1959, a 7.3 magnitude earthquake struck west of Yellowstone National Park. Campers fled in horror while geologists stationed in the area scrambled to document the phenomenon. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) was keen on monitoring the Yellowstone Volcano, a supervolcano that could wreak untold destruction in the event of an eruption. Nobody anticipated the earthquake at that moment.
In the wake of the disaster, 28 people died while authorities estimate damages to be worth 260 million dollars today.
The horrors of the 1959 earthquake
John D. Sanders was with his wife and two children watching a beauty contest when the quake occurred.
“We all ran outside and headed back to the motel. When we got there we saw people jumping out of windows wearing towels and bathrobes. Water was spurting from broken pipes,” he told at the time.
Another witness, Mildren Green, was close to the landslide that was responsible for most of the 28 casualties. The landslide was triggered in Madison Canyon, in which about 50 million cubic yards of debris flowed down the south side of the canyon and halfway up the north side. It partially buried the Rock Creek campground on the valley floor and blocked the Madison River, causing water to back up behind it and creating Earthquake Lake in southwestern Montana.
Greene was camping with her family when a huge stream of muddy water and debris swept over their campsite. Her husband managed to grab the hand of their son and save him just in time. A trained nurse, she became busy tending to the people in the area and said she was the luckiest person there.
“I was busy, I didn’t have to worry about what had happened or what was going to happen.”
“It was a marvelous opportunity for a beginning geologist,” he said in 2008.
Aside from Earthquake Lake, the earthquake also left scarps — a line of cliffs that grow out of the ground due mainly to earthquakes — on Hebgen Lake, Red Canyon faults and, partially, the Madison Fault.
Earthquakes are different from other natural hazards because they persist even after the main event. Aftershocks are very common and can be as deadly as the earthquake that precedes them. In other cases, however, aftershocks could persist even decades after an earthquake.
The team also did not see any signs of magma and other fluids moving beneath the ground, which may otherwise cause the northern cluster swarms.
They noted that aftereffects occurring after such a long time are not completely unheard-of. For one, co-author Guanning Pang previously investigated aftershocks from the 1983 Borah Peak earthquake in central Idaho, some of which are estimated to be as recent as 2017.
“Earthquakes don’t happen as a single discrete event in time,” added co-author Keith Koper.
Sources include:
Express.co.UK
USGS.gov
Seismo.Berkeley.edu
YellowStoneInsider.com